Desmos (Physics)
Numerical Odinary Differential Equation
Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations are methods used to find numerical approximations to the solutions of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Here, the ODEs in most of these works are in the form \[\frac{d^n}{dt^n}\,\vec{y}\left(t\right)=\vec{f}\left(\vec{y},\vec{y}',\ldots,\vec{y}^{(n)},t\right),\] and if we define a new vector \[\vec{Y}= \begin{pmatrix}\vec{y}\\\vec{y}'\\\vdots\\\vec{y}^{(n-1)}\end{pmatrix} \quad\Rightarrow\quad \frac{d}{dt}\vec{Y}=\begin{pmatrix}\vec{y}'\\\vec{y}''\\\vdots\\\vec{y}^{(n)}\end{pmatrix} =\frac{d}{dt}\vec{Y}\] , we may reduce the equation to \[\frac{d}{dt}\vec{Y}=\vec{F}\left(\vec{Y},y\right),\] where \[\vec{F}\left(\vec{Y},y\right)=\begin{pmatrix}\vec{y}'\\\vec{y}''\\\vdots\\\vec{f}\left(\vec{y},\vec{y}',\ldots,\vec{y}^{(n)},t\right)\end{pmatrix}.\]
Classical Dynamics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. Here, most of these work gover the theme like
- Netonian Mechanics
- Electromagnetism
- Special Relativty
- Orbital mechanics

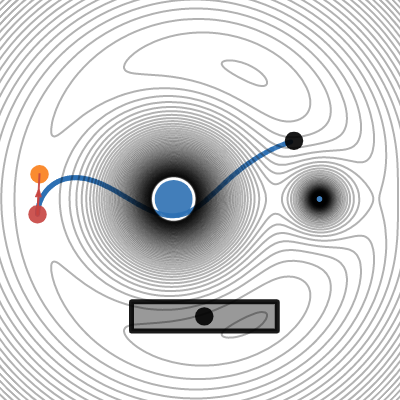 3D problem in rotating system
3D problem in rotating system
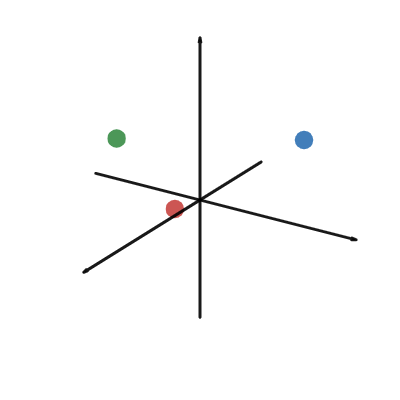 3 body probblem
3 body probblem
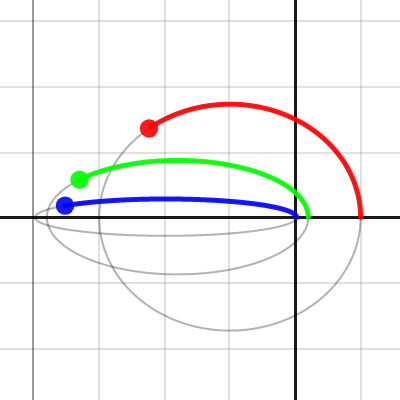 Orbit
Orbit
 sliding pendulum
sliding pendulum
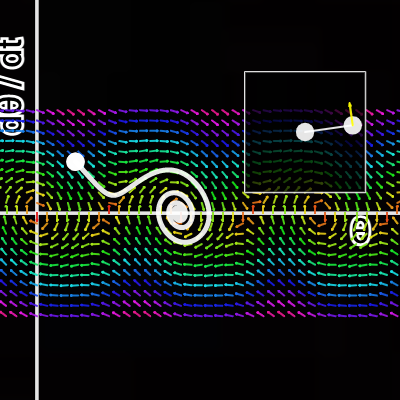 pendulum
pendulum
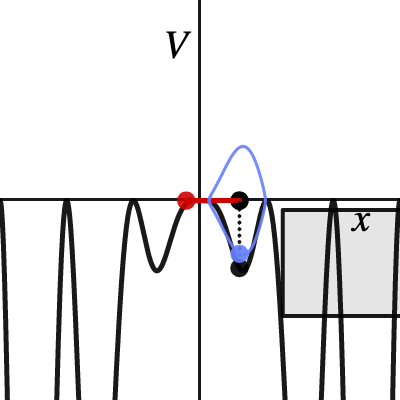 numerical solution of different potential
numerical solution of different potential
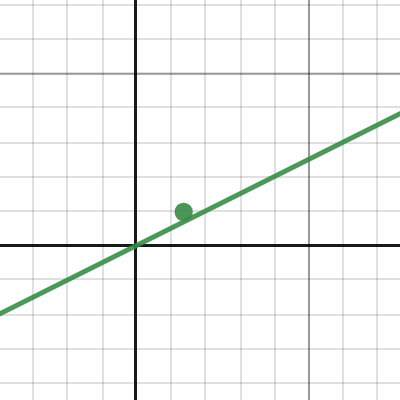 Iteration
Iteration
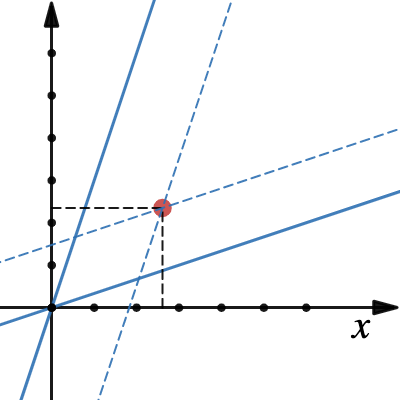 space time diagram
space time diagram
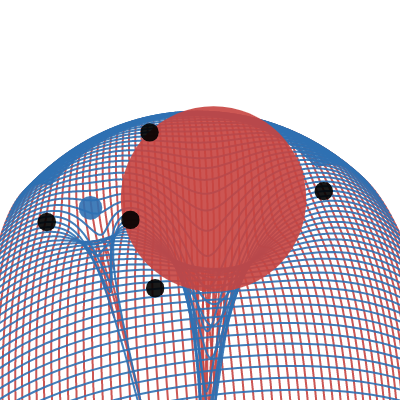 3Body restricted potential in 3D
3Body restricted potential in 3D
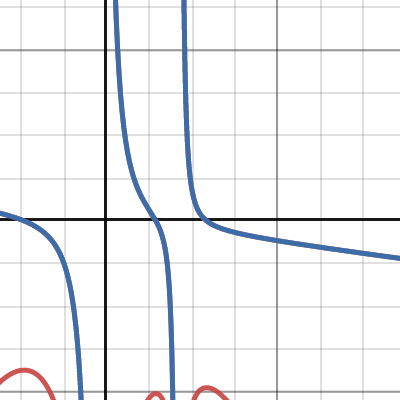 solving lagrangian point
solving lagrangian point
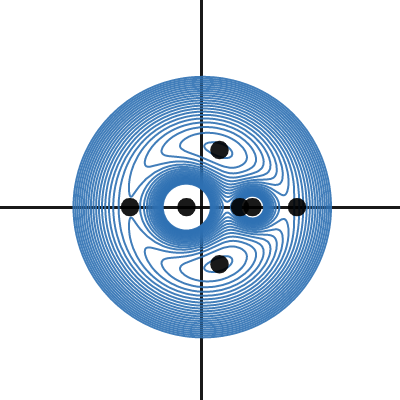 3Body restricted in equal potential palne
3Body restricted in equal potential palne
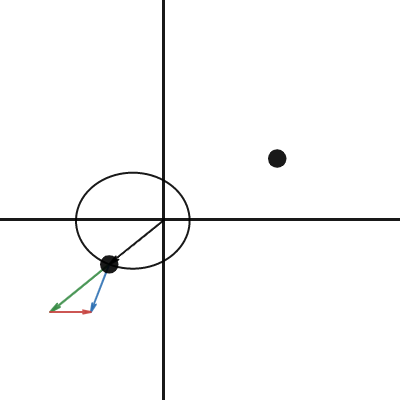 LRL in Kepler
LRL in Kepler
 Bath sink
Bath sink
 Quadratic friction
Quadratic friction
 Motion in EM and gravitational fields
Motion in EM and gravitational fields
 satellite to reach the Earth
satellite to reach the Earth
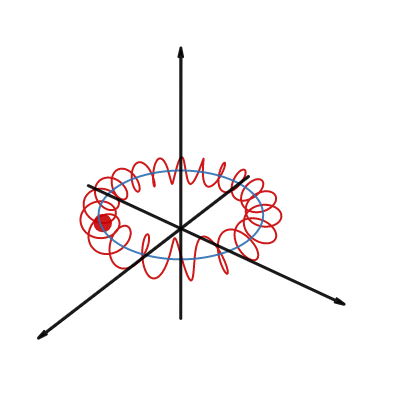 HW6 4
HW6 4
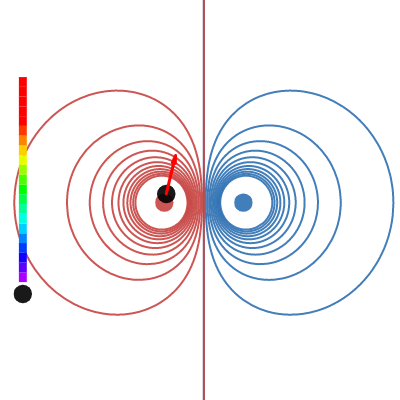 Field line
Field line
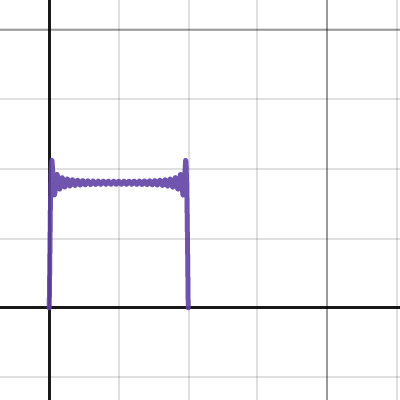 Laplace equation
Laplace equation
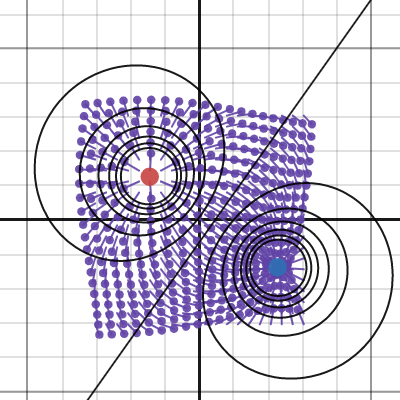 magnetic Filed line
magnetic Filed line
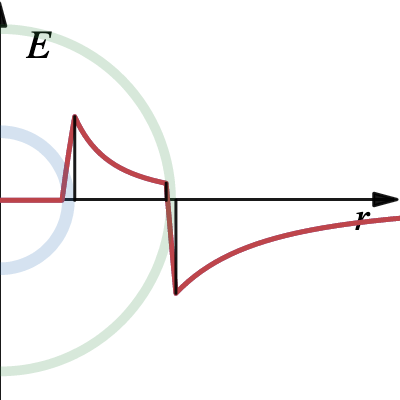 spherical shell electric field
spherical shell electric field
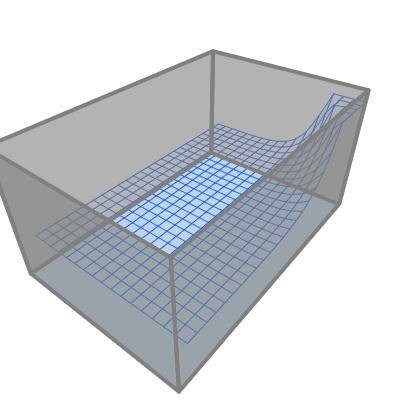 2D Fluid Physics
2D Fluid Physics
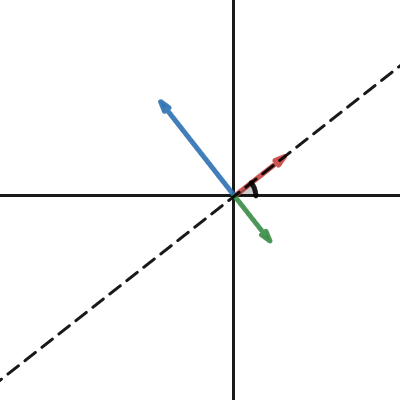 vector of phasor
vector of phasor
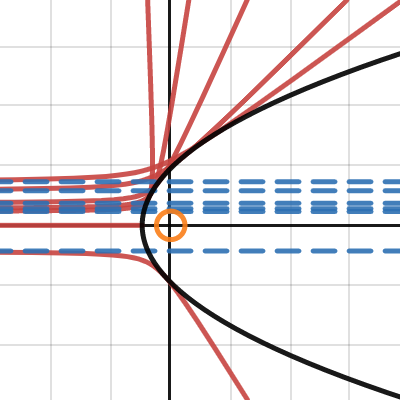 粒子散射
粒子散射
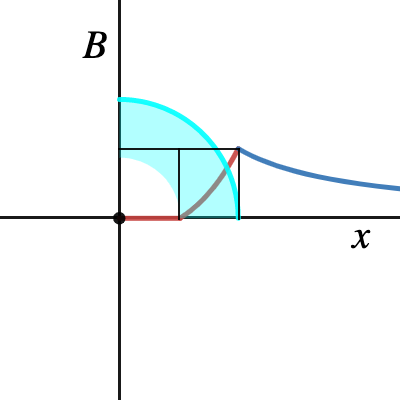 期中考考題
期中考考題
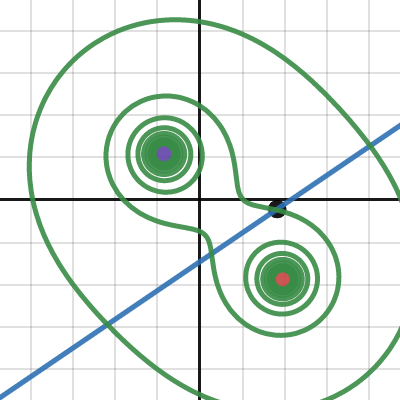 電力線
電力線
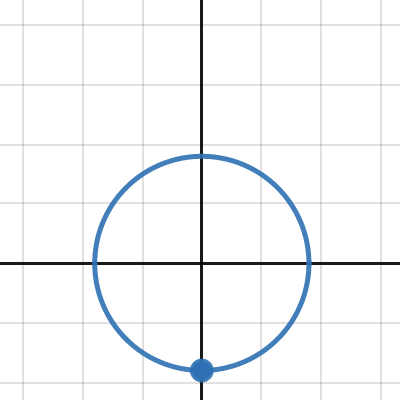 Vertical Circular Motion
Vertical Circular Motion
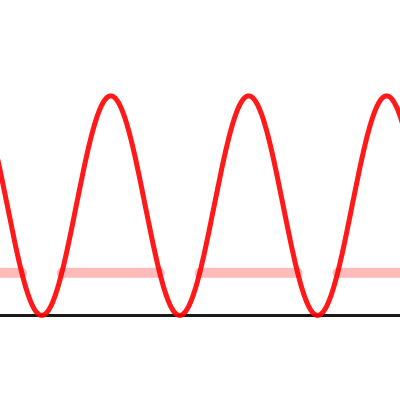 Explain width of wave
Explain width of wave
 ESR
ESR
 Infinite well perturbation
Infinite well perturbation
 Hydrogen
Hydrogen
 Spherical Harmonic
Spherical Harmonic
 Integration of Spherical Harmonic
Integration of Spherical Harmonic
 Hydrogen energy
Hydrogen energy
 氫原子徑向方程
氫原子徑向方程
 potential
potential
 做圖專用(作業)
做圖專用(作業)
 位能簡諧震盪近似模型(cubic spline)
位能簡諧震盪近似模型(cubic spline)
 做圖專用
做圖專用
 tan做圖專用
tan做圖專用
 finite well
finite well
 Spherical Laplace equation 2Dimension
Spherical Laplace equation 2Dimension
 Infinite well Schrdinger equation non sigma
Infinite well Schrdinger equation non sigma
 S6 Particle in a box time dependent Schrdinger equation
S6 Particle in a box time dependent Schrdinger equation
 Double Pendulum (from internet)
Double Pendulum (from internet)
 Hydrogen wave function
Hydrogen wave function
 Hydrogen wave function
Hydrogen wave function
 hydrogen orbital wavefunction
hydrogen orbital wavefunction
 hy test if it will break down
hy test if it will break down
 hy
hy
 地磁偏轉
地磁偏轉
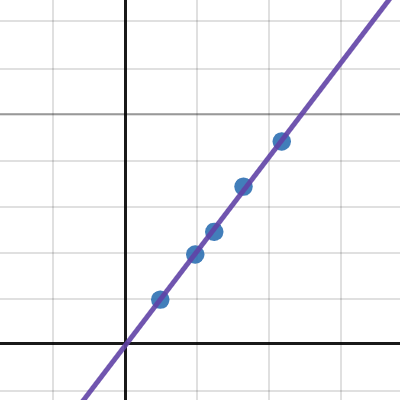 庫侖定律實驗
庫侖定律實驗
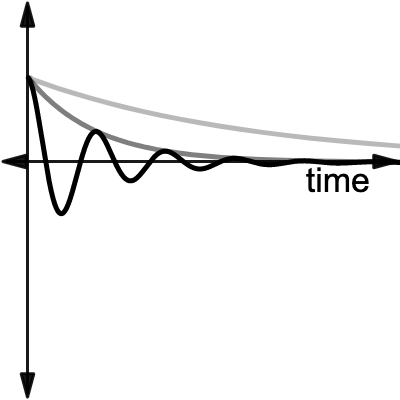 damping
damping
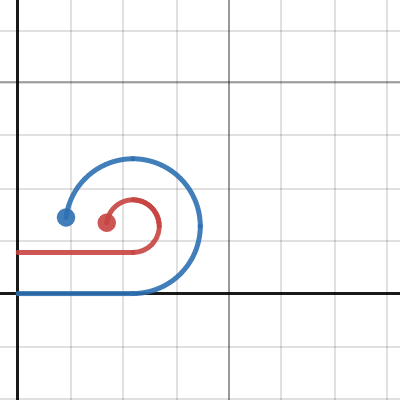 小球大球滾動與非純滾動
小球大球滾動與非純滾動
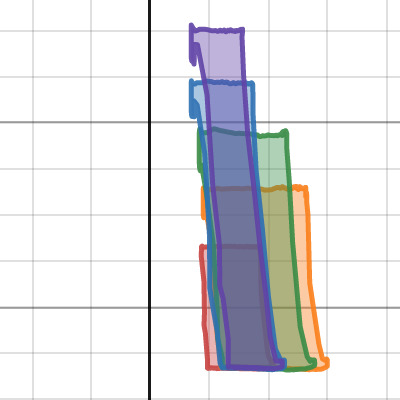 計算離散數據面積熱機實驗
計算離散數據面積熱機實驗
 化學報告
化學報告
 化學報告
化學報告
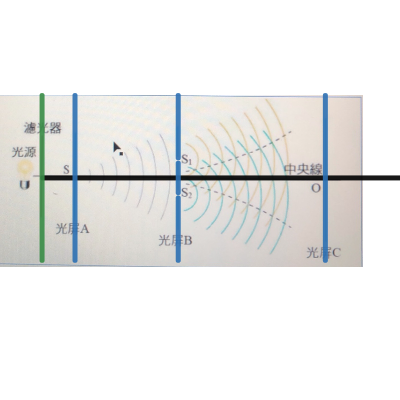
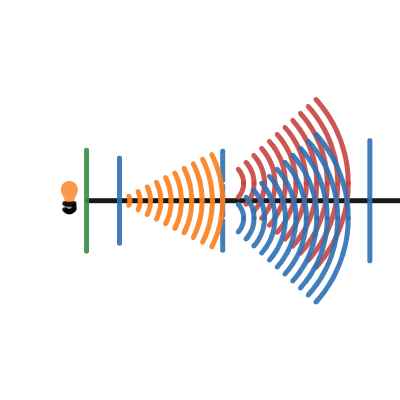 雙狹縫
雙狹縫
 作圖用
作圖用
 光程差
光程差
 楊氏係數
楊氏係數
 實驗
實驗
 實驗
實驗
 電流天秤
電流天秤
 Phase space
Phase space
 普物實驗 重力常數測定實驗
普物實驗 重力常數測定實驗
 普物第一題
普物第一題
 普通物理學實驗二
普通物理學實驗二
 experiment
experiment
 實驗
實驗
 普化實驗四
普化實驗四
 Graphing Calculator
Graphing Calculator
 普化實驗二
普化實驗二
 化學實驗01
化學實驗01
 作業
作業
 door damping
door damping
 tilted throwing on slope
tilted throwing on slope
 Gravity
Gravity
 vertical falling
vertical falling
 vertical droping int process
vertical droping int process
 Drop
Drop
 vertical falling
vertical falling
 vertical droping
vertical droping
 Kick flip
Kick flip
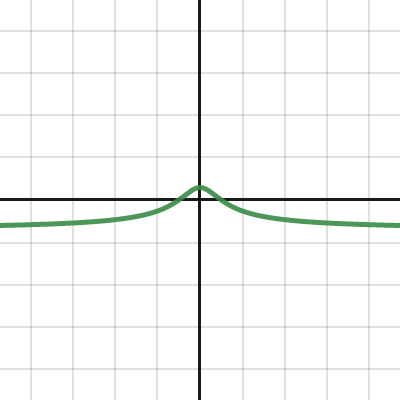 Gravity SHM
Gravity SHM
 線圈磁場 平面積分
線圈磁場 平面積分
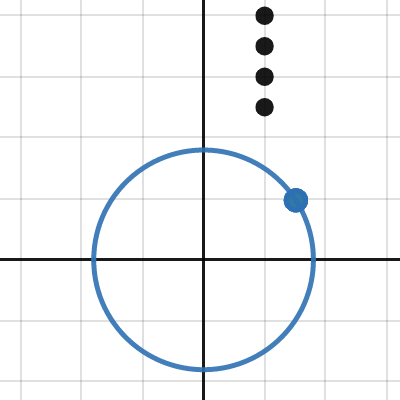 Vertical Circular Motion
Vertical Circular Motion
 線圈磁場 空間積分
線圈磁場 空間積分
 磁場積分
磁場積分
 旋轉
旋轉
 必過兩點之結果
必過兩點之結果
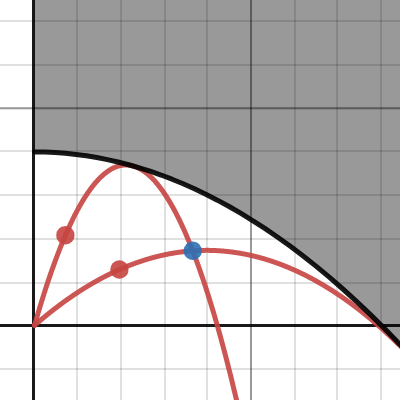 拋物線必過之點
拋物線必過之點
 粒子散射
粒子散射
 粒子散射
粒子散射
 粒子散射
粒子散射
 Blackbody radiation law
Blackbody radiation law
 ollie analyze
ollie analyze
 磁力線空中
磁力線空中
 干涉
干涉
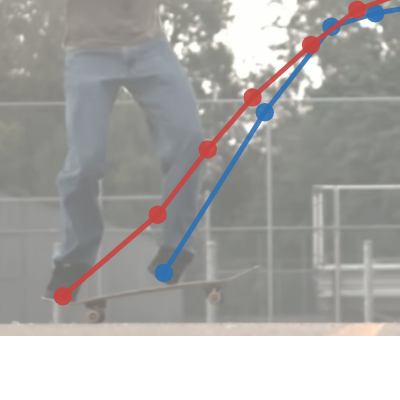 ollie
ollie
 ollie
ollie
 馬克士威_波茲曼速率分佈
馬克士威_波茲曼速率分佈
 視深
視深
 震動
震動
 重疊波
重疊波
 透射波 常態分佈 測試
透射波 常態分佈 測試
 磁力線
磁力線
 透射波 Cos 測試
透射波 Cos 測試
 光陰影
光陰影
 電子軌道能量圖
電子軌道能量圖
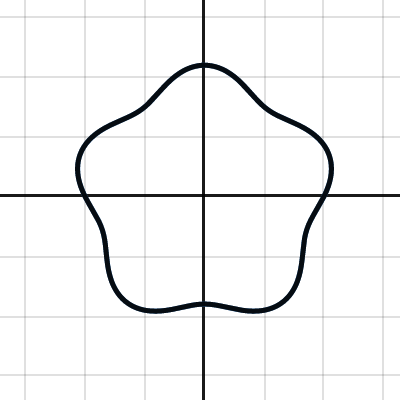 圓形駐波
圓形駐波
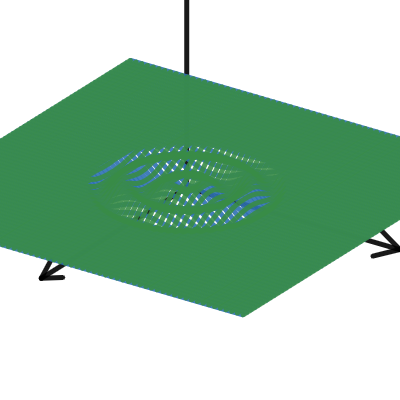 觀察
觀察
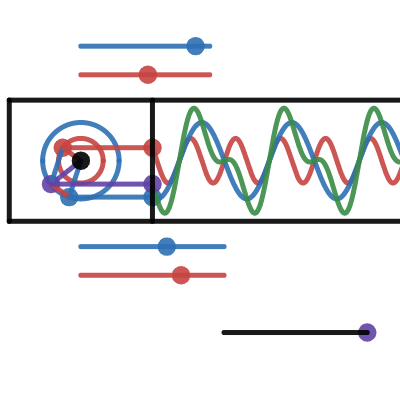 相量
相量
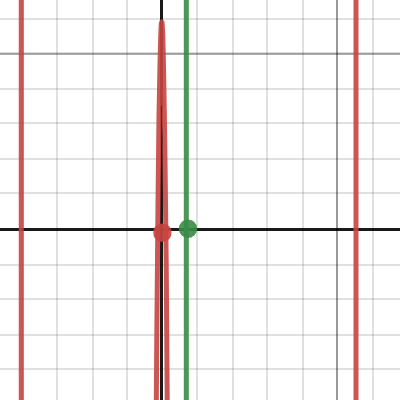 結果
結果
 疊加
疊加
 透射波 常態分佈
透射波 常態分佈
 波動
波動
 三維波模擬
三維波模擬
 尖波
尖波
 駐波
駐波
 透射波 cosxt
透射波 cosxt
 雙狹縫
雙狹縫
 數據亂數
數據亂數
 分配
分配
 What ever
What ever
 位能
位能
 分子震動
分子震動
 視深
視深
 折視
折視
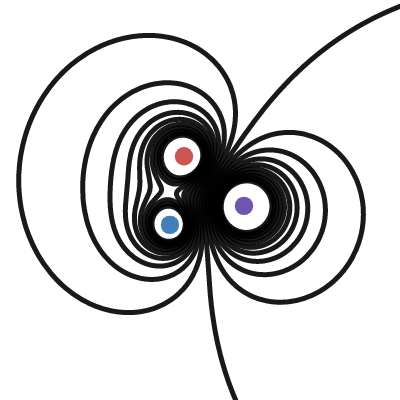 Electric potential 2
Electric potential 2
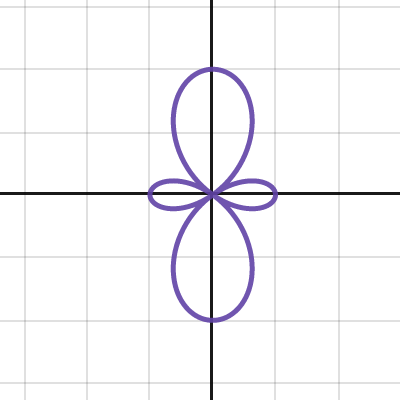 類氫原子
類氫原子
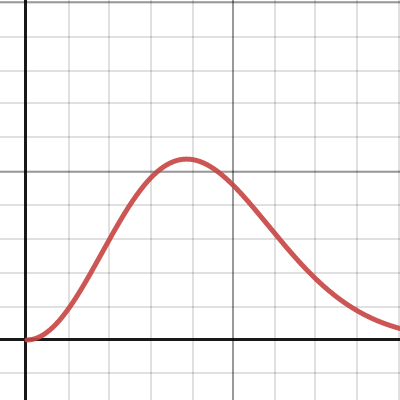 馬克士威分佈
馬克士威分佈
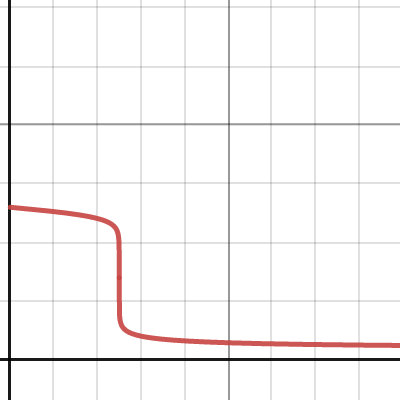 鹼酸滴定
鹼酸滴定
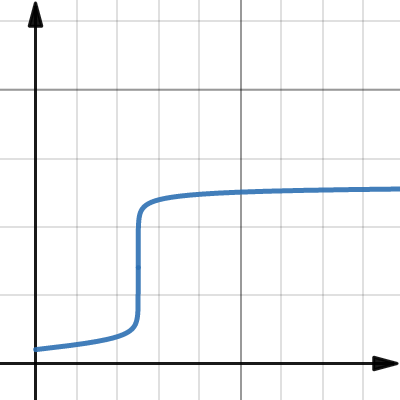 酸鹼滴定
酸鹼滴定
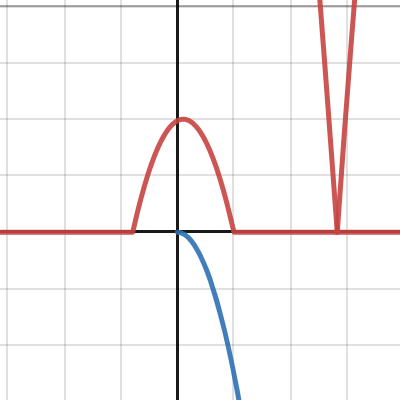 恢復係數彈跳
恢復係數彈跳
 化學作業
化學作業
 拋出旋轉體軌跡
拋出旋轉體軌跡
 物質波函數
物質波函數
 泛音
泛音
 化學作業
化學作業
 化學
化學